Announcements
Drinks
Spain's robust growth amid expected fiscal adjustments
By Jakob Suwalski, Sovereign and Public Sector Ratings
We have revised upwards our 2024 GDP growth forecast for Spain (A-/Positive) from 1.9% to 2.4%, following stronger-than-anticipated export dynamics and resilient private consumption in the first half of the year, outperforming euro area peers (Figure 1). For 2025, we expect slightly lower growth of around 2.2%, reflecting primarily our anticipation of fiscal adjustments.
The Spanish economy outperformed our expectations in the first quarter with quarter-over-quarter GDP growth of 0.7%, against our forecast of 0.5%. This positive trend continued into the second quarter, with the economy expanding by 0.8% according to preliminary data, indicating an underlying resilience in the country’s economic structure.
Figure 1. Spain’s economy outperforms euro area
Year-on-year, %
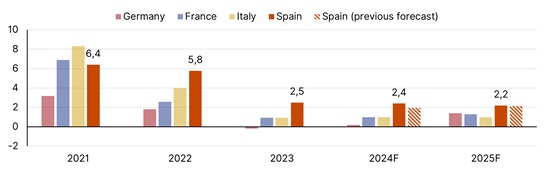
Sources: Eurostat, Scope Ratings
Key drivers behind Spain's robust economic performance
Spain’s labour market has seen significant expansion, which is critical to sustaining long-term economic growth. The significant growth in the active population since 2019 is driven primarily by immigration, particularly from South America, and labour market reforms that have yielded marked gains in participation rates.
These reforms have enhanced flexibility, job quality, and reduced unemployment, improving labour market dynamics. Notably, much of 2023's new employment was attributed to foreign-born individuals, underscoring immigration's key role in strengthening Spain's job market. The services sector, including finance and manufacturing, has been instrumental in boosting labour productivity.
One factor contributing to the upward growth revision for 2024 is the performance of Spain's service exports. Despite global economic challenges, prices for exported services from Spain have increased at a slower rate than those of competitor countries. This competitive pricing strategy has enabled Spain to capture a growing share of the global non-tourism service exports market.
Additionally, Spain's industrial and export outlook is promising, supported by signs of recovery in key sectors across the euro area, notably in Germany (AAA/Stable). This industrial revitalisation is likely to support overall euro area exports, with Spain positioned to benefit.
Another element underpinning Spain’s economic strength is the substantial support from EU funds, particularly Recovery Funds aimed at mitigating the impacts of the pandemic and supporting long-term resilience. This financial support has enabled Spain to undertake necessary investments in infrastructure, technology, and green energy sectors, allowing for public finance consolidation without undermining economic vitality. To date, Spain has received EUR 48bn in grants of the overall EUR 163bn (around 11% of GDP) envelope from the European Commission.
Over the past decade, Spain has capitalised on historically low interest rates to deleverage both its sovereign and private sectors. Pro-active debt management has led to improvements in the country's credit profile and debt affordability. With interest rates trending downward once again, Spain is well-placed to leverage these favourable conditions to support growth-enhancing investments, which remain modest to GDP.
Improved labour market drives revenue growth, yet higher spending warrants fiscal adjustments
Since the pandemic, Spain has recorded significant improvements in government revenues to GDP. By 2023, government revenue increased by about 3% of GDP compared to 2019, primarily due to higher income taxes, which supports efforts to rebuild fiscal buffers and reduce debt. This resilience marks a stark contrast to the fiscal repercussions of the Global Financial Crisis, which saw steep declines that took years to recover from.
Figure 2. Budget dynamics improve, but expenditure growth still a challenge
EUR bn (LHS), % of GDP (RHS)
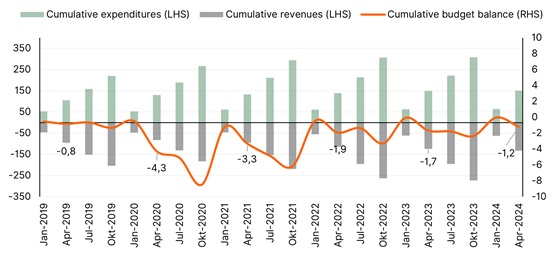
Sources: Ministerio de Hacienda, Scope Ratings
Resilient tax revenues can largely be attributed to a robust recovery in the labour market characterised by significant employment gains and inflation, along with effective policy measures such as VAT rate adjustments and job retention schemes.
Looking ahead, a portion of the post-2019 revenue increase is expected to persist, influenced by phased pension reforms expected to support social security contributions. In addition, recent inflation led to nominal wage increases, triggering a fiscal drag effect that has boosted personal income tax revenues. However, despite strong revenue growth, significant expenditure led to a substantial budget deficit of 3.7% in 2023 and an expected 2.8% in 2024.
Spain's regional budgets are crucial for the country's future fiscal trajectory
Significant disparities in budget performances and debt levels across Spain's autonomous regions underscore the need for comprehensive reform to enhance fiscal health. To tackle these disparities, reforming the fiscal framework that governs regional spending and borrowing is crucial.
Despite the November 2023 agreement between Spain’s socialist party (PSOE) and the Catalonian party ERC to assume EUR 15bn of debt from the Fondo de Liquidez Autonómico (FLA), the main channel for financing regional governments, concerns remain that this unconditional debt relief could lead to systemic overspending at the regional level.
However, this situation could also act as a catalyst for more profound reforms affecting the revenue-expenditure (mis)match of regions, potentially leading to more sustainable fiscal practices across Spain’s autonomous communities.
With Spain's public debt at 107.7% of GDP at the end of 2023 and expected to gradually decline, enhancing fiscal resilience through strategies that support economic growth and control public spending is vital. Thus, it is imperative that the government fosters consensus around reforms, particularly those affecting sub-sovereign frameworks and stimulating GDP growth.
Scope’s next scheduled review date for the Kingdom of Spain is 6 September 2024.
Make sure you stay up to date with Scope’s ratings and research by signing up to our newsletters across credit, ESG and funds. Click here to register.







